RIGID BODY TRANSLATION
Rigid body translation is the type of motion in which all points of the body move in a plane that remains parallel to a fixed reference plane.
Translation represents a combination of two simplest motions:
-
translation
-
rotation about an axis whose direction is fixed but whose position in space changes over time.
During rigid body motion, all its parts move in the same way and follow the same trajectories.
Examples of Rigid Body Translation
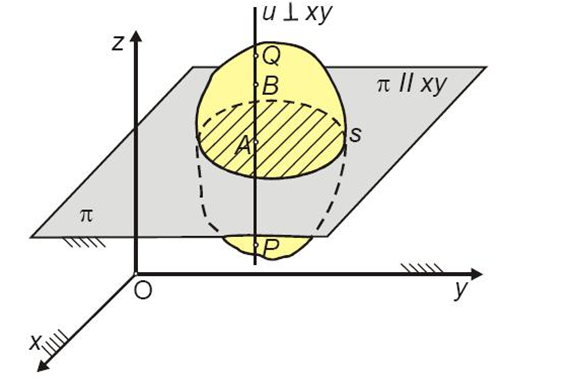
We observe the positions of the cross-section S at times t0, t1, and t2
(noting the material line and its positions):
Rigid body translation consists of two fundamental motions: translation
and rotation about an axis passing through a chosen point in the plane of the figure S perpendicular to that plane.
Moving the representative cross-section from one position to another can be achieved
-
by one translation (of the section along with point C) and one rotation about point C by an angle φ
or
-
by a single rotation about the same axis of rotation.